The Importance of Inflation
Inflation is a critical economic indicator that affects the purchasing power of consumers, investment decisions, and overall economic growth. Recently, inflation rates have surged worldwide due to various factors including supply chain disruptions, increased demand post-pandemic, and geopolitical tensions. In the UK, understanding the current inflationary landscape is essential for households and businesses alike.
Current Inflation Rates
As of October 2023, the UK’s inflation rate stands at 6.5%, down from a peak of 11.1% in October 2022. This decrease signals a gradual stabilization of consumer prices following the extraordinary spikes experienced during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic and the ongoing effects of the war in Ukraine, which has impacted energy prices significantly. The Bank of England has implemented a series of interest rate increases to combat inflation, raising the base rate from 0.10% in December 2021 to 5.25% in September 2023.
Causes of Inflation
The primary contributors to the current inflation in the UK include supply chain bottlenecks, rising energy prices, and increased costs of raw materials. Additionally, demand has rebounded strongly, driven by a surge in consumer spending as restrictions have eased. This phenomenon, known as demand-pull inflation, occurs when demand surpasses supply. Additionally, wages have begun to rise in many sectors, contributing to cost-push inflation, where businesses pass on increased labour costs to consumers.
Impact on Consumers
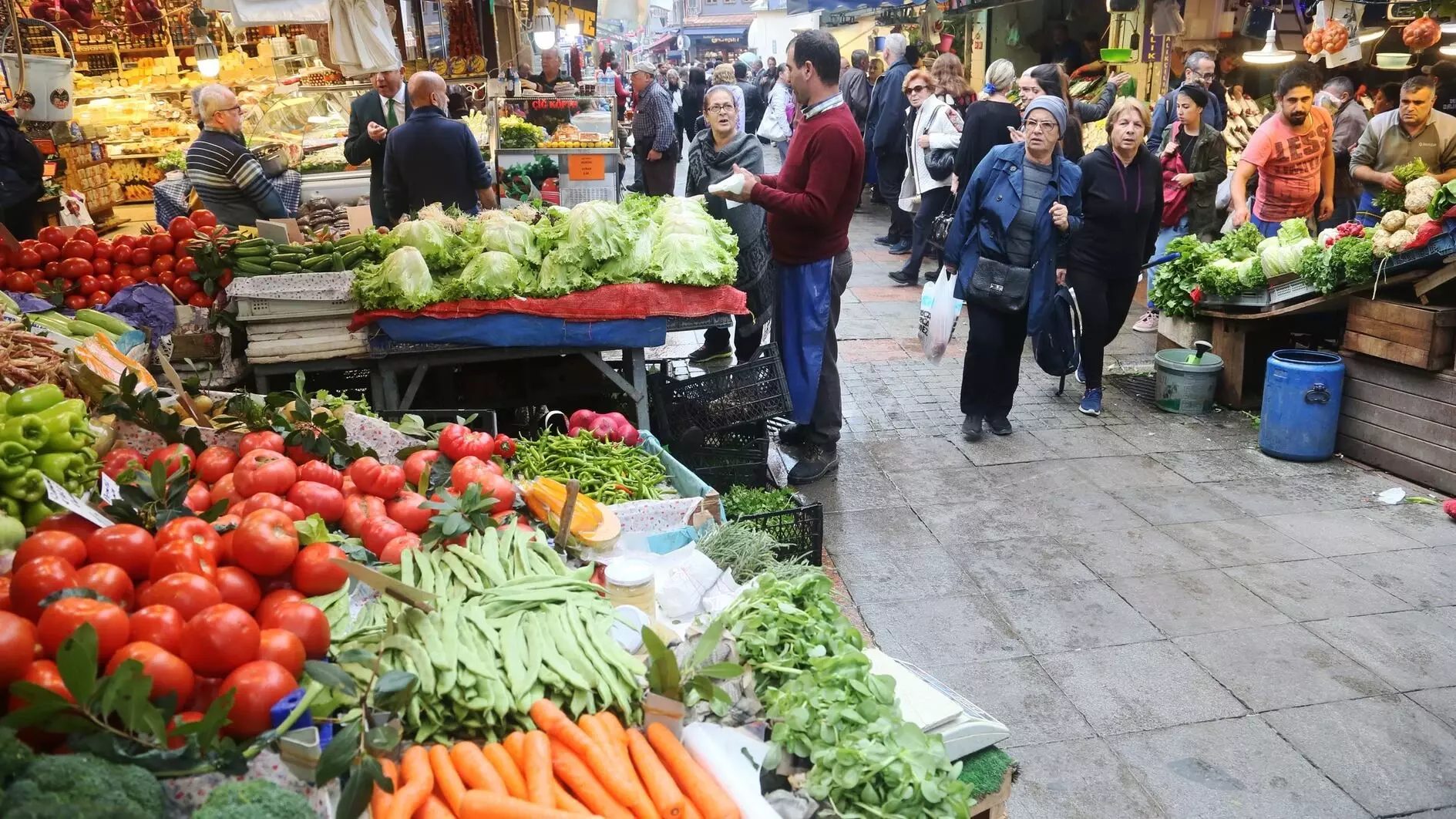
For the average consumer, prolonged inflation translates into increased prices for essentials like food and energy, eroding household purchasing power. Recent reports indicate that food prices have risen by over 15% year-on-year, significantly impacting lower-income households. The heightened cost of living has led many to adjust their spending patterns, prioritising essential items while cutting back on non-essentials.
Future Outlook
Economists predict that inflation will continue to decrease gradually as the effects of past monetary policy manifest and global supply chains improve. The Bank of England is anticipated to remain cautious in its approach to interest rates, balancing the need to control inflation with the risk of slowing economic growth. For consumers, it will be crucial to stay informed and adapt to the changing economic landscape, as inflation’s trajectory will undoubtedly influence financial planning and spending habits.
Conclusion
Understanding inflation and its implications is vital for anyone navigating the current economic climate. As trends evolve and policymakers respond, consumers must remain vigilant about their financial decisions. With potential shifts in inflation expected, how households and businesses adapt could pave the way for future economic resilience in a post-pandemic world.