Introduction
Inflation in the United States has been a focal point of economic discussion over the last few years, particularly as the nation continues to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic. Understanding the factors contributing to inflation, its current trends, and its broader implications is essential for both consumers and policymakers.
Current Trends in US Inflation
As of September 2023, the inflation rate in the United States, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), has shown signs of moderation but remains a concern. Recent data indicates that the inflation rate stands at approximately 3.7%, down from a peak of 9.1% in June 2022. This decline is primarily attributed to easing supply chain disruptions and stabilising energy prices.
However, the Federal Reserve continues to monitor core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices; this remains higher at around 4.3%. The persistence of elevated core inflation suggests that while overall price growth may be slowing, underlying pressures are still present.
Factors Influencing Inflation
Several factors contribute to the current state of inflation in the US. First is the ongoing labour market tightness, with unemployment rates hovering near 3.5%. This situation creates upward pressure on wages, which can contribute to inflation if productivity does not keep pace.
Additionally, geopolitical tensions and supply chain disruptions, particularly in energy and agriculture, have kept prices elevated. The recent conflicts in Eastern Europe and their impact on global oil and gas supplies have been particularly significant. Furthermore, consumer spending remains robust, partly fuelled by increased savings rates during the pandemic.
Impact on Consumers and the Economy
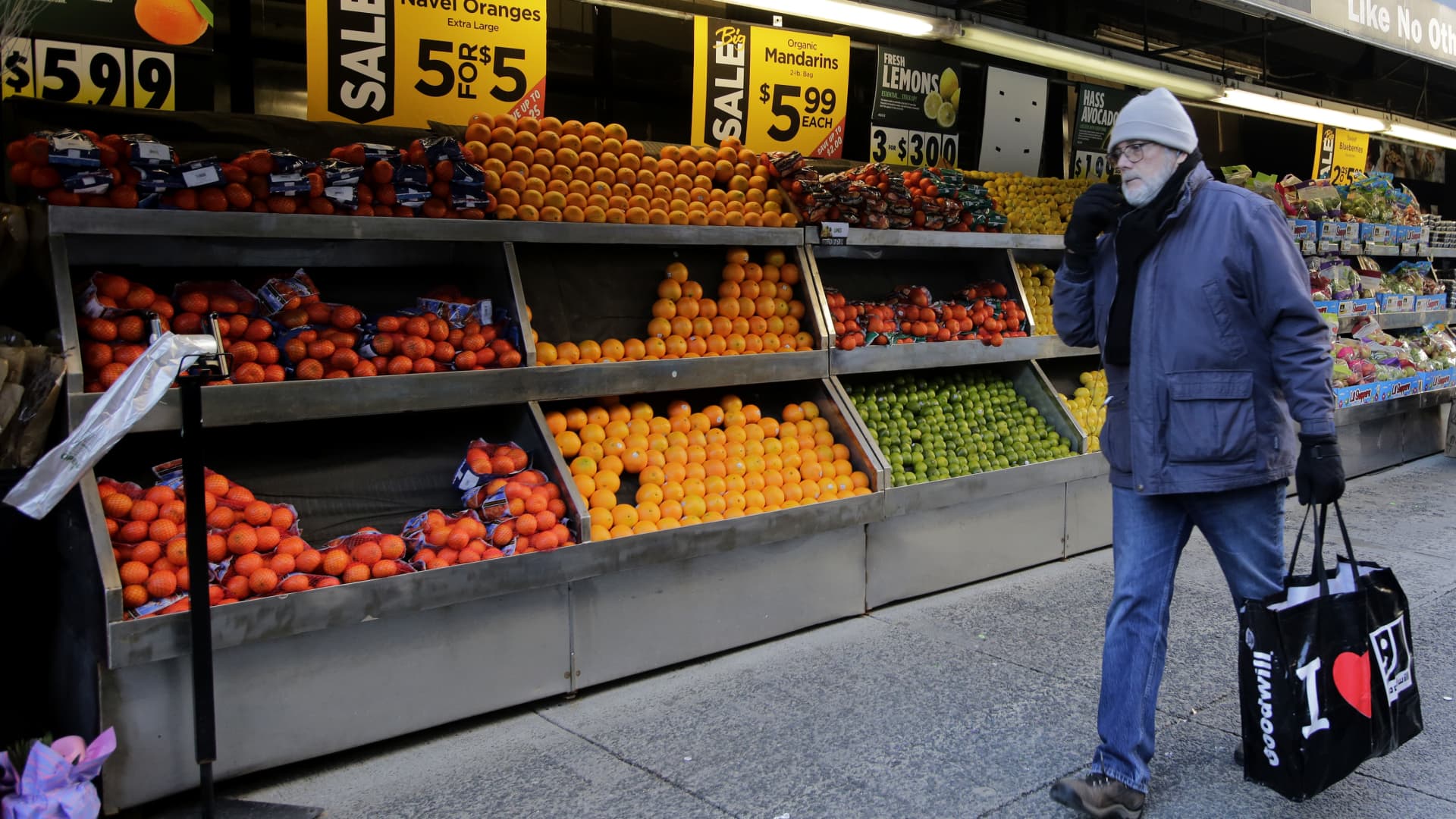
The ramifications of inflation are significant for consumers, particularly concerning the rising cost of essentials such as food, housing, and transportation. Despite wage growth, many households are experiencing a decline in real purchasing power, leading to financial strain. The Federal Reserve’s measures to combat inflation, including interest rate hikes, aim to moderate spending and borrowing, which could have long-term implications for economic growth.
Conclusion
As we move into the final months of 2023, the outlook for US inflation remains pivotal in shaping both economic policy and consumer behaviour. While recent trends indicate a cooling in inflation rates, underlying pressures persist, necessitating cautious optimism. For consumers, understanding these dynamics is crucial as they navigate the challenges of increased living costs. Continued monitoring and adjustments by the Federal Reserve will be essential in addressing inflation and ensuring economic stability.