Introduction
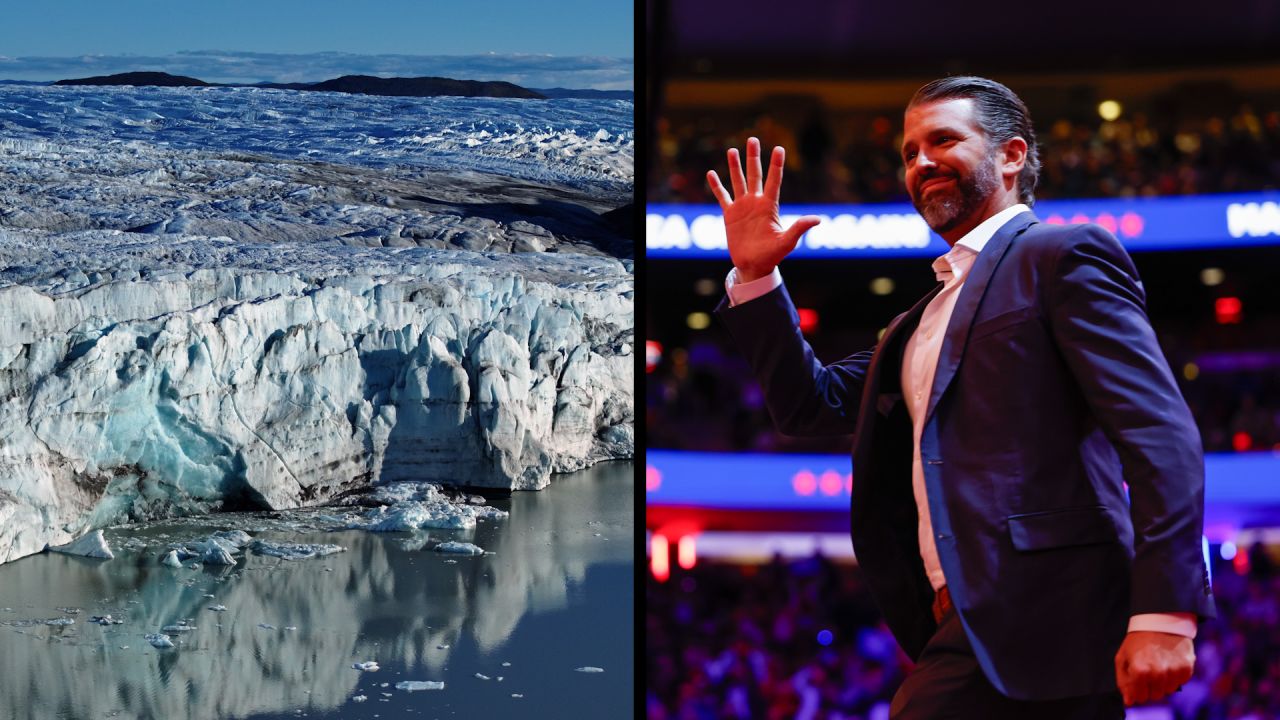
The prospect of former President Donald Trump purchasing Greenland in 2019 became one of the most discussed geopolitical topics of that year. Trump’s interest highlighted the strategic importance of the island, which is rich in natural resources and a significant geographical asset in the Arctic region. This discussion not only caught the attention of political analysts but also raised questions about the implications for US foreign relations and Arctic sovereignty.
The Proposal and Its Reception
In August 2019, reports surfaced that President Trump had expressed interest in buying Greenland from Denmark, framing it as a lucrative business opportunity due to the island’s vast mineral resources and strategic location. The proposal was met with a mix of incredulity and outright rejection from various stakeholders, including the Danish government, which labelled the idea as absurd. Former Prime Minister Lars Løkke Rasmussen referred to the idea as a “commercial interest that has nothing to do with love for Greenland.” This backlash did not deter Trump, who later described the island as “a great place”, drawing attention to its potential for economic development.
Potential Implications of the Purchase
The conversation around Greenland raised important considerations regarding the islands’ indigenous populations, the governance structure, and the long-lasting implications of a potential sale. Greenland is an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, with its own political system and a significant degree of self-governance. Any attempt to purchase the island would face enormous logistical and ethical challenges, considering the rights and aspirations of the Greenlandic people.
Geopolitical Context
Trump’s interest in Greenland can also be understood within a broader geopolitical context. As climate change influences Arctic dynamics, the region is opening up to resource extraction, shipping routes, and strategic military positioning. Major powers, including China and Russia, are increasingly focused on the Arctic, which makes Greenland a focal point in various international discussions on security and environmental concerns. Experts argue that rather than seeking to purchase territory, the US should focus on cooperation with Denmark and Greenland to address common challenges in the Arctic, such as climate change and sustainable development.
Conclusion
While the idea of the US purchasing Greenland was ultimately shelved, the discussions it sparked about Arctic strategy remain pertinent today. Looking forward, the emphasis should be on collaborative approaches that respect the rights and governance of the Greenlandic people. As climate change continues to alter the geopolitical landscape of the Arctic, understanding this significance extends beyond mere territory acquisition and towards sustainable international relations.