Introduction
China has emerged as a global leader in renewable energy, spearheading the development of wind farms across the nation. The importance of this transition to wind energy cannot be overstated, as it plays a pivotal role in combating climate change, reducing reliance on fossil fuels, and achieving energy security. With ambitious targets for carbon neutrality by 2060, China’s investment in wind energy is critically relevant in the wake of growing environmental concerns.
Current Developments in China’s Wind Energy Sector
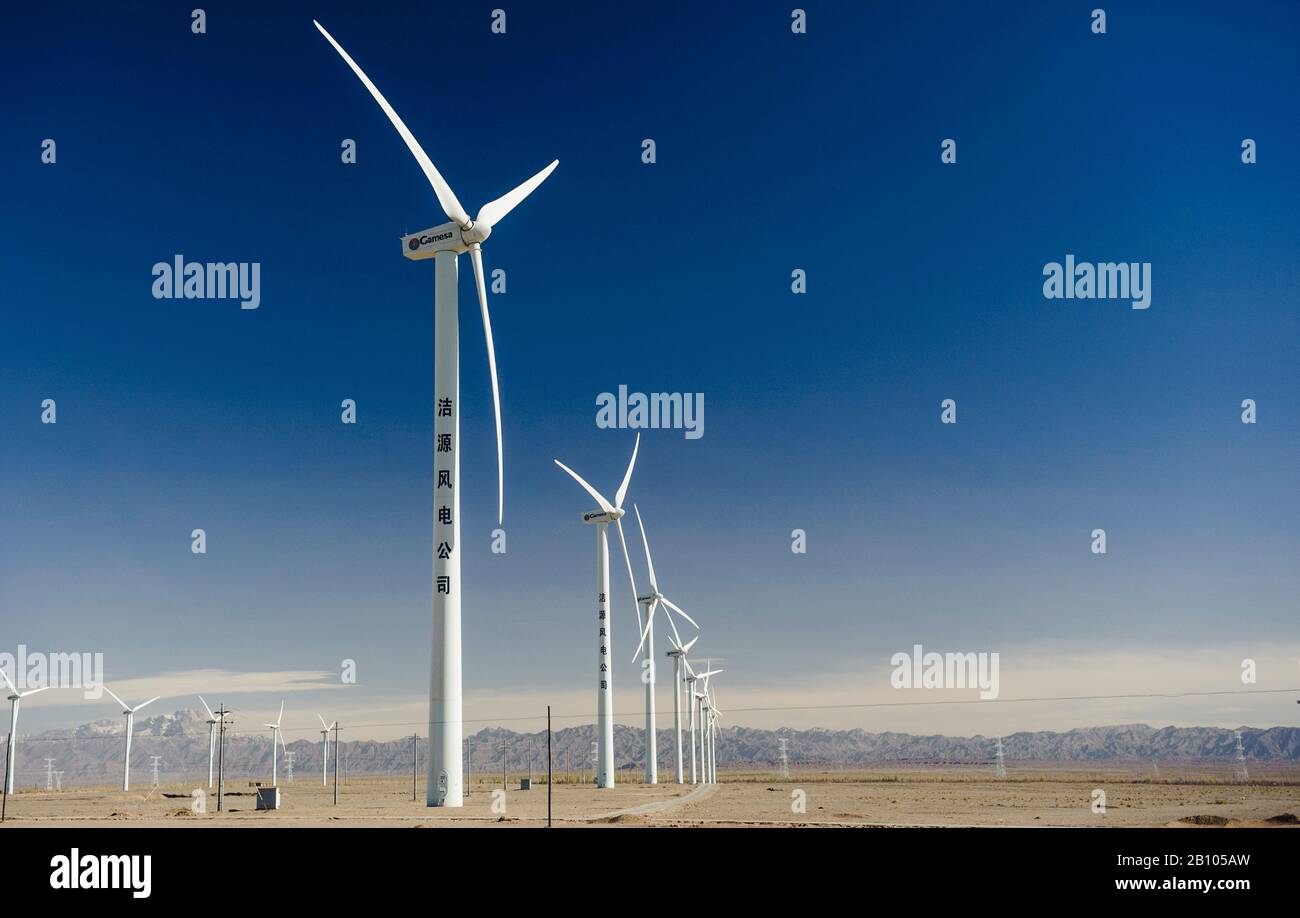
As of 2023, China boasts the largest installed wind power capacity in the world, exceeding 300 gigawatts (GW). Recent reports from the Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC) indicate that China installed over 60% of the world’s new wind installations last year. This growth is largely fueled by government policies promoting clean energy, including subsidies and support for innovation in wind turbine technology.
Significant projects highlight China’s commitment to expanding wind farms. For instance, the Gansu Wind Farm, one of the largest in the world, is expected to reach an installed capacity of 20 GW, providing power to millions while reducing carbon emissions. Additionally, offshore wind farms have gained traction, with ambitious plans for installing an estimated 50 GW in the coastal regions by 2030.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite these achievements, the wind energy sector in China faces challenges. Issues such as grid connectivity, localized energy distribution, and integration of renewable sources remain hurdles. Additionally, as more projects are initiated, concerns over land use and environmental impacts are increasingly prominent. Addressing these challenges will be crucial as China forges ahead with its wind energy initiatives.
Looking to the future, experts predict that China’s wind farms will continue to flourish, contributing significantly to the country’s transition to a low-carbon economy. As technology advances and costs decline, the integration of wind energy into the national grid is expected to improve, enhancing energy accessibility and sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, China’s wind farms represent a substantial step towards achieving a sustainable future. With strategic investments and policies, the nation is not only bolstering its energy independence but also making a significant impact on global efforts to mitigate climate change. For readers worldwide, the developments in China’s wind energy sector serve as an inspiring example of renewable energy’s potential to reshape energy landscapes and provide ecological benefits in the fight against climate change.