Introduction
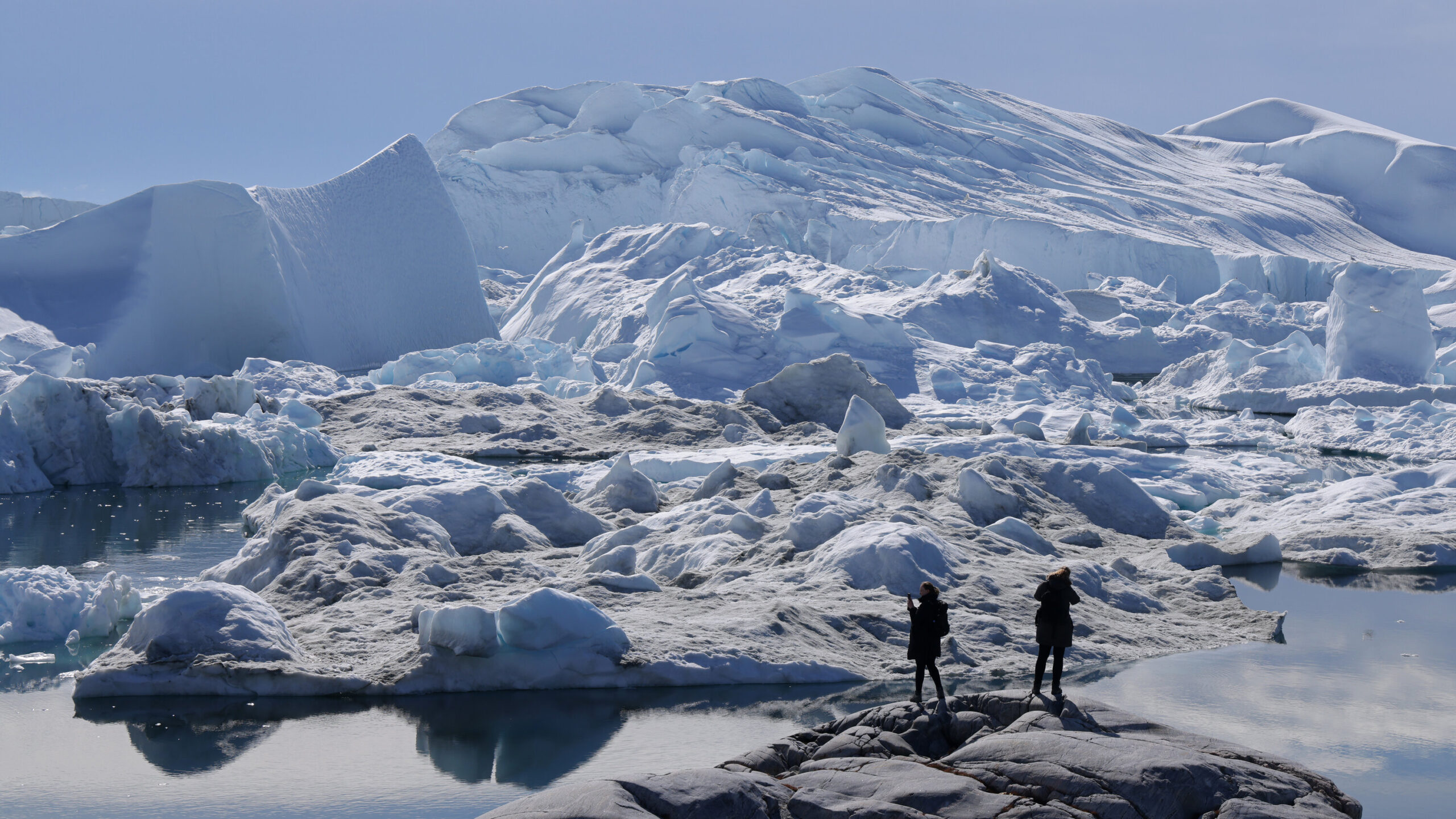
In recent years, the topic of Greenland has made headlines, particularly during former President Donald Trump’s administration, when he expressed interest in acquiring this vast Arctic territory. Greenland, the world’s largest island, has become a focal point of geopolitical interest due to its abundant natural resources, strategic location, and the implications of climate change. But why does Trump want Greenland, and what significance does it hold in the broader context of international relations?
The Geopolitical Context
Greenland, a semi-autonomous territory of Denmark, is known for its vast reserves of natural resources, including rare earth minerals and oil. The Arctic region has been gaining attention as melting ice opens up new shipping routes and access to untapped resources. Trump’s consideration of purchasing Greenland can be seen as a strategic move to assert U.S. dominance in the Arctic, a region where both Russia and China have increased their presence.
Trump’s Vision for Greenland
In 2019, during a visit to Denmark, Trump made headlines when he publicly suggested that the U.S. might purchase Greenland. This proposal was met with mixed reactions, including ridicule from Danish officials and concerns from international analysts. Trump viewed the acquisition as a ‘real estate deal’ that could bolster American influence in the Arctic. The former President has expressed admiration for the area’s resources and its potential for economic development.
Implications for International Relations
The U.S. interest in Greenland goes beyond mere territorial acquisition. It reflects a broader strategy to counterbalance the influence of China and Russia in the Arctic. Both nations have been actively expanding their military and economic presence in the region, raising concerns about sovereignty and environmental protection. By emphasizing its interest in Greenland, the U.S. aims to strengthen its alliances with Denmark and other Arctic nations, signalling a commitment to cooperation in the face of growing global competition.
Conclusion
Trump’s interest in Greenland underscores the intersection of climate change, resource competition, and geopolitical strategy. The potential acquisition of Greenland could reshape U.S. engagement in the Arctic and influence global power dynamics. As the world continues to grapple with the implications of climate change, understanding the motivations behind Trump’s desire to acquire Greenland becomes increasingly significant. Whether this interest evolves into concrete actions or remains a point of political discourse, it serves as a reminder of how territorial ambitions can be intertwined with pressing global issues.